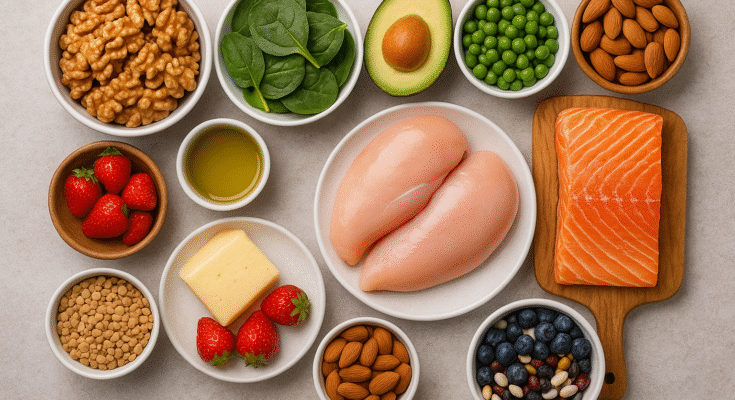
Nutrition is the foundation of health, fitness, and overall well-being. What we eat not only provides energy for daily activities but also influences body composition, mental clarity, immunity, and long-term health. Proper nutrition is about balance, quality, and timing, rather than restrictive dieting or quick fixes.
What Is Nutrition?
Nutrition is the science of how food affects the body. It involves:
- Providing essential nutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals)
- Supporting growth, repair, and energy production
- Regulating metabolic and physiological functions
- Preventing deficiencies and chronic diseases
Good nutrition is not just about eating “healthy”—it’s about eating smart for your body’s needs.
Why Nutrition Is Important
- Supports energy levels – Proper nutrition fuels workouts, work, and daily tasks.
- Promotes body composition – Balances fat loss and muscle gain.
- Boosts immunity – Essential nutrients support the immune system.
- Improves mental health – Brain function relies on proper vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Enhances longevity – Reduces risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic illnesses.
Key Components of Nutrition
1. Macronutrients
- Carbohydrates – Primary energy source (fruits, grains, vegetables)
- Proteins – Muscle repair, growth, and enzyme production (meat, fish, eggs, legumes)
- Fats – Hormone regulation, brain health, and energy (nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish)
2. Micronutrients
- Vitamins – Support immune function, metabolism, and tissue repair
- Minerals – Important for bone health, hydration, and nerve function
3. Water
- Vital for hydration, digestion, nutrient transport, and temperature regulation
4. Fiber
- Promotes gut health, digestion, and satiety
Nutrition for Fitness and Body Composition
- Protein intake: 1.6–2.2 g per kg body weight for muscle growth and repair
- Calorie balance:
- Slight deficit for fat loss
- Slight surplus for muscle gain
- Meal timing: Spread protein intake across meals for optimal muscle synthesis
- Hydration: Drink adequate water to support metabolism and performance
Healthy Eating Tips
- Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables
- Prioritize lean protein sources and healthy fats
- Limit added sugars and highly processed foods
- Eat whole grains instead of refined grains
- Control portion sizes and practice mindful eating
- Avoid skipping meals; maintain consistent energy levels
Sample Balanced Daily Nutrition Plan
Breakfast: Oatmeal with nuts, seeds, and berries
Snack: Greek yogurt with fruit
Lunch: Grilled chicken, quinoa, and mixed vegetables
Snack: Hummus with carrot sticks or a handful of almonds
Dinner: Baked salmon, brown rice, and steamed broccoli
Hydration: 2–3 liters of water throughout the day
Tips for Long-Term Nutrition Success
- Focus on consistency over perfection
- Adjust food intake based on activity level, goals, and body changes
- Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues
- Combine nutrition with regular exercise for optimal results
- Educate yourself about food labels and nutrient quality
Conclusion
Nutrition is the cornerstone of health, performance, and longevity. By focusing on balanced meals, nutrient quality, and hydration, you can fuel your body for energy, strength, and overall well-being. Good nutrition is not a short-term diet—it is a lifelong habit that shapes your health, fitness, and quality of life.